14/10/2025
Excellent design goes far beyond making things look attractive. Design is about solving the right problems in the right way. The greatness of a design starts long before mockups and wireframes, with the way we brief designers.
A good brief will save days of rework, minimize misunderstandings, and energize stronger products. Beyond the brief itself, however, there is something even more powerful and that is collective understanding in the team and with the client. Without such collective understanding, even the strongest ideas will prove inadequate.
A Brief Is Not Just a Task List: It Is a Bridge
Far too often, a design brief is reduced to one or two words:
- "Add filters to search."
- "Create a new onboarding flow."
- "Design a new page for the new product."
While these instructions describe what to do, they rarely explain why it matters. Effective design needs more than tasks; it needs context, clarity, and a shared purpose. A strong brief connects business goals, user needs, and design decisions.
It outlines why something needs to be created, for whom we are building it, what problem we are solving, and how the work fits in the big picture.
Without that connection, design risks becoming a “make it look nice” exercise instead of a strategic problem-solving process.
When designers understand the motivations behind business goals and user behaviors, they become active contributors rather than task executors. That’s when design moves from simply creating visuals to shaping meaningful solutions.
Understanding as a Business Advantage
From years of product development, we know that shared understanding is not a soft skill, it is a competitive edge.
Every unclear expectation at the start of a project can turn into days of redundant rework. Every missing detail in a brief can turn into misaligned features. Every "this is not what we had in mind" moment usually reduces to too little shared understanding.
In fact, Forbes shared that clear design frameworks (like detailed wireframes and flows) reduce ambiguity and back-and-forth by around 30%, leading to smoother and more cost-effective development. Moreover, according to a Hypersense report, fixing misunderstandings after delivery costs up to 100x more than clarifying them upfront. That is why we invest heavily in alignment from day one.
For example, if a client requests “a dashboard for reporting,” we could start designing right away. But without understanding who will use it, why they need it, and what success looks like, we risk creating something visually appealing but practically useless.
When the context is missing, good design fails to deliver business value.
That is why we challenge designers and clients to ask questions, question assumptions, and think of the big picture together. This sets the project up for success without delays.
How to Write a Brief That Works?
A good brief needs to be thoughtful. The goal to provide information and create a shared understanding between the business, designers, and other stakeholders. There are five essential questions we always cover before starting design:
- Who is the user? What do they need, want, and hate?
- What is the business goal? How does this feature or page create impact?
- What is the context? Where does this element fall in the user journey?
- What are the constraints? Branding constraints, technical restrictions, time constraints.
- What can we reference? Current patterns, past work, competitor solutions.
These insights allow designers to deliver solutions that are both beautiful and strategic, and generate business value.

The Client's Role in the Process
Great design is a collaborative process. We collaborate very closely with customers to fully understand their vision, challenges, and priorities.
We ask challenging questions, share early concepts, and validate assumptions with you. That early alignment eliminates surprises later and results in products that meet business goals and user needs.
Customers continuously tell us that they value designers as partners, not just implementers. And that partnership is based on trust, and trust is based on understanding.
In Conclusion - Better Briefs, Better Products
Design starts with understanding. A well-written brief creates alignment, reduces risk, and leads to better decision-making.
When all stakeholders, from clients to designers and teams, are aligned, products ship faster, collaboration works more effectively, and the final outcome offers more value to the business and to the user.
Ultimately, an amazing brief is about building knowledge. That's where amazing design begins.
23/09/2025
According to recent studies, over 90% of executives believe their business model needs to change within the next three years to remain competitive in the digital economy. Yet, many organizations still struggle to define what digital transformation truly means, often confusing it with simple automation or the adoption of new tools.
The reality is that digital transformation goes far beyond technology. It represents a fundamental shift in how companies operate, deliver value to customers, and adapt
It’s important to distinguish the terms:
How To Know If You Need Digital Transformation
Many companies realize the need for digital transformation only when everyday challenges start to slow them down. These warning signs are often easy to spot, but they must be addressed in time to avoid bigger obstacles.
Common signs your business may need digital transformation:
The Four Phases of Digital Transformation
Once the need for digitalization becomes clear, the next step is to understand what the journey involves. Having a clear picture of the stages helps set realistic expectations, allocate resources effectively, and ensure that the transformation delivers long-term value.
While the phases are common across industries, what makes the difference is how they are executed. Here’s how we guide our clients through each stage, ensuring that strategy, technology and people work together to deliver lasting impact.
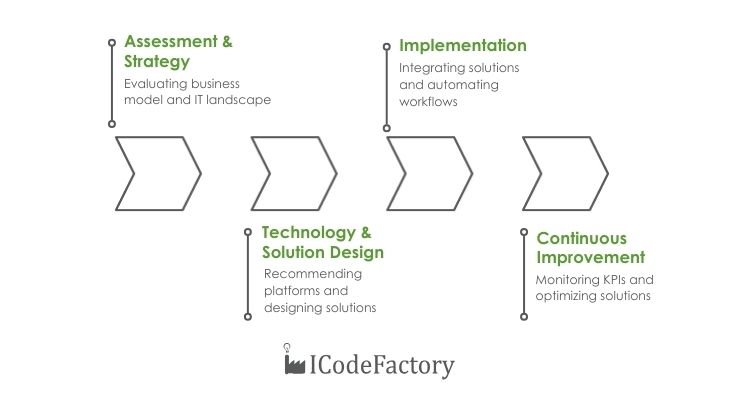
1. Assessment & Strategy
Every transformation starts with clarity. We start by understanding your business model, goals, and challenges. This includes evaluating your current IT landscape, identifying gaps in digital maturity, and benchmarking against industry leaders. The outcome is a clear digital vision with measurable KPIs and a roadmap that links technology investments directly to business value.
2. Technology & Solution Design
Once a clear strategy is established, the next step is to translate it into the right technological approach. This can involve recommending established platforms, such as cloud services, ERP or CRM systems and automation tools, to support the organization’s goals efficiently. In cases where standard solutions do not fully address specific needs, a tailored software solution can be designed to align precisely with the company’s processes and objectives. Throughout this phase, careful attention is given to integrating new systems with existing IT infrastructure, defining a robust data architecture, and ensuring that both scalability and security are built into the design from the outset.
3. Implementation
Execution is where strategy becomes reality. We integrate or develop the right solutions, automate workflows and align processes to reduce inefficiencies. Cybersecurity and regulatory compliance remain central throughout, ensuring a smooth and secure rollout.
4. Continuous Improvement
Transformation doesn’t end at launch. We continuously monitor KPIs, track user adoption, and use feedback to refine and optimize solutions. As your business grows, we expand its capabilities. Whether that’s adding AI-driven insights, IoT integrations, or new digital channels. This ensures your transformation is not a one-time project but an ongoing source of competitive advantage.
Core Areas of Impact
Digital transformation impacts multiple aspects of your business. Here are the core areas where it delivers the most value:
-
Process automation – Streamline workflows, reduce manual work, and free up your team for high-value activities. By automating repetitive tasks like invoice approvals or order processing, your employees can focus on strategic initiatives that drive growth.
-
Cloud migration – Scale resources as needed and cut infrastructure costs. Moving systems and applications to the cloud improves accessibility, enables remote collaboration, and reduces the burden of maintaining on-premises infrastructure.
-
E-commerce & digital channels – Expand market reach and modernize sales models. Digital channels allow you to reach new customer segments, offer personalized experiences, and quickly adapt your offerings to changing market demands.
-
Data & analytics – Base decisions on insights, not assumptions. By centralizing data and applying analytics, you can uncover patterns, forecast trends, and make evidence-based decisions that improve performance across all departments.
-
Customer experience – Offer faster, tailored services that keep clients coming back. Personalization, self-service options, and seamless interactions increase customer satisfaction and loyalty, while also reducing support costs.
While these areas offer clear benefits, every company’s journey is different. There is no universal blueprint for digital transformation. The right plan is tailored to your industry, your strategic priorities, and the people who drive your business. Successful transformation requires aligning technology with business goals, ensuring that each step creates measurable value.
Choosing the Right Technology Partner
Digital transformation is not only about tools and processes. It is also about finding a partner you can rely on throughout the process. The right partner brings technical expertise, but just as important, they provide transparency, flexibility, and a clear understanding of your business goals. A reliable partner helps you avoid costly mistakes, accelerates implementation, and ensures long-term results.
How to recognize a good partner:
Still Not Sure If This Is For You?
If you are still uncertain whether digitalization is the right step for your business, or you believe the need has not yet arrived, it helps to look at the concrete benefits it brings—and the risks of postponing it.
Benefits of digitalization:
Risks of not digitalizing:
Digital transformation is a journey, not a one-time project. Understanding its stages, recognizing the signs that change is needed, and choosing the right technology partner are essential steps to ensure that your organization not only keeps pace with the market but also creates long-term value. Taking informed action today lays the foundation for a more efficient, flexible, and resilient business tomorrow.
Ready to take the next step?
Let's explore how our expertise can help you innovate and implement your vision in a digital world.
Reach out to us: ICodeFactory | Contact
09/09/2025
Would you build a house without a blueprint?
Most people wouldn’t. The same logic applies to building software.
Starting development without first laying a solid design foundation can feel efficient at first, but it often leads to miscommunication, shifting requirements, and missed opportunities to create real value for users.
More companies are realizing that thoughtful design upfront helps teams stay aligned, reduce surprises, and make the most of their budget and timeline.
In this post, we’ll walk you through why a design-first approach helps you move faster, reduce risk, and build the right thing from the start.

Design isn’t just about adding decoration, it’s about shaping smart solutions from the start
Good product design doesn’t just make your product “look better.” It helps your business make smarter decisions before development even starts.
When teams invest in product discovery, user research, and prototyping early on, they’re able to:
Design isn't a nice-to-have. It’s what transforms a list of ideas into a product that works. For your users and your business.
What companies risk when they skip design
Many companies, especially those under tight timelines, jump straight into development. That often leads to:
Worse, some products never make it to market at all, not because they weren’t technically feasible, but because they weren’t solving the right problem to begin with.
Why design makes development faster (yes, really)
A thoughtful design process might feel like a delay, but in reality, it speeds everything up.
Many studies have shown that design-led teams are able to:
Moving fast is important, but only if you're heading the right way. That’s where design makes all the difference.
What a design-first software partner looks like
When looking for a development partner, you want more than just coders. You need a team that understands the business context and helps shape your product early on.
At ICodeFactory, we take a design-first approach to software development:
This approach helps our clients build user-centered products that deliver measurable business value, without overspending or missing deadlines.
When should you involve design?
Before the first line of code.
Before the budget is locked.
Before the team starts building something they can’t easily change later.
Whether you’re starting fresh or modernizing an existing system, design gives you the clarity, speed, and flexibility you need to succeed.
Skipping design always costs more than doing it right the first time.
Let’s build something that works. By designing it first.
Ready to take the next step?
Let's explore how our expertise can help you innovate and implement your vision in a digital world.
Reach out to us: ICodeFactory | Contact
19/08/2025
In any initiative, there’s a strong temptation to jump straight into action. When goals are ambitious and expectations are high, moving quickly feels like the right move.
But in the rush to deliver, many organizations overlook a critical phase. One that can make or break the outcome:
Product Discovery.
Too many teams assume they already know what users want. Stakeholders demand quick wins, budgets tighten, and discovery gets sidelined. The result? It’s like launching a rocket without a clear trajectory. You may move fast, but miss your target.
The cost is more than just losing time. It’s misaligned decisions, wasted resources, and products that fail to deliver real value. Importantly, investing in product discovery is typically far cheaper than going straight to development and risking wasted resources on unwanted features.
Product discovery creates the space to pause, reflect, and align. It’s not about slowing down. It’s about steering your efforts in the right direction. Asking the right questions early reduces risk, improves outcomes, and builds confidence and clarity.
The Business Value of Discovery
Discovery is your reality check: Are you building something people will use and pay for?
Here’s how it delivers real value:
Cuts Risk: Test assumptions early to avoid costly mistakes and wasted effort.
Speeds Time-to-Market: Align on the right problem from the start for faster, focused development.
Boosts Alignment: Creates shared goals across business, product, and tech teams, reducing friction.
Sharpens Prioritization: Uses real user insights and data to focus resources on what truly matters.
The result? Smarter investments, better outcomes and more efficient use of time and budget.
What Discovery Looks Like in Practice
While tools and techniques may differ, the core steps of product discovery stay the same:
- Define the problem: What exactly are we solving and why does it matter for the business?
This step cuts through guesswork. By involving stakeholders, analysing the market, and uncovering hidden barriers, you build a rock-solid foundation for what comes next.
- Understand the users: Who are we really building for and what do they care about most?
Discovery brings real users into the conversation through interviews, surveys, and observation. It reveals pain points and unmet needs that data alone cannot show. These insights ensure your design hits the mark, not just your assumptions.
- Map the opportunity: Where can we create the biggest impact for users and the business?
This is where insights turn into strategy. Using tools like journey maps and value proposition canvases, teams connect user needs with business goals. The outcome is a clear, focused view of the best opportunities to chase.
- Test ideas early: How can we learn fast without risking too much?
Discovery favours quick, low-risk experiments. Instead of building full products upfront, teams test ideas with prototypes, mock-ups, or simulations. This saves time and money by validating what works before major investments.
- Align on scope and priorities: What do we build first and why?
Armed with real insights, teams decide what matters most. Priorities are based on evidence, not opinions. This creates alignment across teams and sets a clear, confident path forward.

When Skipping Discovery Becomes Expensive
Skipping discovery may seem like a shortcut. It only delays critical questions until later stages, when answers cost more. Common consequences include:
- Misaligned expectations
- Poor product-market fit
- Wasted resources
- Slower, reactive decision-making
Discovery as an Ongoing Process
Discovery works best as a continuous practice that keeps teams curious, responsive, and aligned with evolving user needs.
Continuous discovery helps you stay ahead, not just catch up.
By revisiting assumptions, testing new insights, and validating direction regularly, teams reduce the risk of costly rework and keep their solutions aligned with real-world needs.
How the Right Partner Makes It Easier
Embedding this mindset into your organization takes more than intention. It takes the right approach and the right support.
At ICodeFactory, we help teams integrate discovery practices throughout the entire product lifecycle. That means bringing structured thinking, proven methods, and real collaboration to every stage, not just at kick-off.
The result?
Smarter decisions. Faster adaptation. And better outcomes that last.
Ready to take the next step?
Let's explore how our expertise can help you innovate and implement your vision in a digital world.
Reach out to us: ICodeFactory | Contact
22/07/2025
From Data to Value: Why Companies Can’t Afford to Ignore Their Data Anymore
Is your company using data for reporting only, or for decision-making?
Modern businesses today have access to more data than at any point in history. But access doesn’t equal understanding, and it certainly doesn’t guarantee value.
The true value lies in what you do with it, how you transform raw information into clear insight and smarter decisions.
That’s the purpose of our newly established Data & AI Lab – to turn raw data into measurable business impact. We’ve built a process that extracts value every step of the way, from data collection to intelligent automation.
Why this matters now
Data is the new oil, but only if you know how to refine it.
Most companies today generate data continuously, through operations, customer interactions, internal tools and digital platforms. When data stays siloed, unstructured, or underused, it can’t support better decisions. It becomes noise instead of guidance.
Meanwhile, companies who refine and use data can:
- Detect problems before they escalate
- Respond to change faster than the competition
- Deliver more value with fewer resources
- Unlock new ideas for growth
And the gap between these two types of organizations is growing.
Our approach: From raw data to business impact
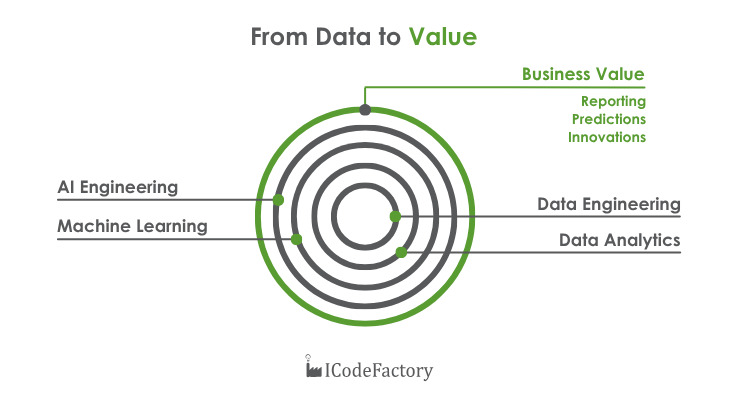
At our Data & AI Lab, we’ve built a structured framework for data transformation. Each stage builds on the previous one, forming a clear path from technical capability to business value.
1. Data Engineering: Build the foundation
Everything starts with strong data foundations. Our engineers collect, clean, organize, and prepare data from diverse sources, ensuring accuracy and reliability. High-quality data is critical. Without it, even the most advanced analytics won’t deliver meaningful results.
2. Data Analytics: Turn numbers into insight
With clean, structured data, we move into the analytics phase. Here, we extract patterns and key findings that support decision-making. Companies using analytics report significant gains:
- Up to 60% reduction in operational errors
- Faster time-to-insight, which leads to quicker market response
- Enhanced customer understanding (57% of companies use analytics to improve customer experience)
3. Machine Learning: Learn and predict
Machine Learning systems use historical data to detect patterns, forecast trends, and make data-driven recommendations. This helps businesses shift from reactive responses to proactive strategies. The value is clear: predictive capabilities reduce uncertainty, automated decisions improve efficiency, and personalized experiences drive stronger customer loyalty.
4. AI Engineering: Build intelligent systems
This is where advanced analytics become part of day-to-day operations. AI-powered systems optimize processes, prevent breakdowns, and automate decision-making across industries. From predictive maintenance to intelligent product design, this phase turns insights into action – autonomously.





What you gain from this process
At the end of this journey, our clients gain:
- Reliable reporting to track key metrics
- Predictive models to plan ahead
- Innovative solutions that open new business opportunities
In short, we help companies shift from data collection to data-driven execution. From reactive to strategic. From uncertainty to insight.
The real question: Can you afford to wait?
In a competitive market, relying on guesswork is no longer an option. Companies that continue to make decisions without real data risk falling behind, not because they lack the data, but because they fail to act on it.
While others use data to streamline processes, organizations that delay risk being left behind. The window for catching up is narrowing, and the cost of inaction is only getting higher.
That’s exactly why we built our Data & AI Lab: to help companies transform idle data into real business value.
If your data is sitting idle, it’s time to put it to work – before someone else does it better.
Ready to take the next step?
Let's explore how our expertise can help you innovate and implement your vision in a digital world.
Reach out to us: ICodeFactory | Contact
24/06/2025
How does industry knowledge shape the quality of custom software?
Behind every great software solution is someone who knows the industry inside and out, guiding every decision.
While technical skills are vital, they alone can’t guarantee that a solution will meet real-world needs.
At ICodeFactory we embed industry professionals directly into our development teams. These individuals bring deep knowledge of the sectors we serve, from banking to insurance to healthcare, ensuring that what we build aligns with business operations, regulations, and user expectations.
This article explores why having domain expertise inside the IT team matters and how it shapes software that meets real business needs.
What a Domain Expert Actually Does
A Domain Expert bridges the gap between business and technology, bringing deep knowledge of a specific industry: its workflows, regulations, and real-world challenges.
Acting as a translator, the domain expert turns business goals into clear priorities for the technical team and explains complex processes in clear terms. By speaking the client’s language and bridging communication gaps, they ensure the software addresses real business needs and fits the industry context while leaving technical details to the developers.
Their input is critical at every stage:
Why Domain Knowledge is as Critical as Technical expertise
While technical expertise is focused on how to build software, domain expertise is about the why should software work a certain way.
They focus on different but equally essential aspects of software development:
|
Technical expertise
|
Domain expertise
|
|
Software development, system design, testing
|
Process design, industry workflows, compliance, user behaviour
|
|
Focused on performance and reliability
|
Focused on real-world application and business fit
|
|
Build the solution
|
Ensures the solution meets all right needs
|
This collaboration reduces misunderstandings and speeds up decision-making at every stage. It makes software not just functional, but also practical and aligned with business goals.

Key Benefits of having Domain Expert
Real Value in Action
Our advantage comes from industry veterans who bring real-world insight to every project. They come from industries where mistakes are costly and rules are strict, such as banking. More than just valuable insight, they offer a foresight. This means they understand not only the terminology but also how decisions are made, what regulators focus on, and which details cannot be overlooked.
As a result, our teams are equipped with:
This leads to a more efficient process, and ultimately, software that is not only built correctly, but built to perform in the real world.
Crafting Solutions That Make Sense
Building the right thing begins with knowing what “right” means.
When your software truly understands your processes, challenges, and objectives, it becomes a powerful tool that drives real results.
Ready to take the next step?
Let's explore how our expertise can help you innovate and implement your vision in a digital world.
Reach out to us:ICodeFactory | Contact
27/05/2025
Imagine your new employees experiencing a seamless, personalized onboarding journey from day one - free of stress, uncertainty, or administrative bottlenecks. Standard onboarding methods often fall short in the age of digital transformation, leading to inefficiencies and talent loss. According to Friedman, it takes just 30 days for new hires to feel welcomed and connected if organizations create a positive environment.
It's noticeable that more companies are open to adopting AI in onboarding to deliver a customized experience and smooth the transition for new hires.
How can AI boost employee engagement, productivity, and deliver tangible value to your company? Up next, we explore how companies can leverage artificial intelligence for long-term success.
Transforming Employee Onboarding with AI
By introducing intelligent systems, organizations can streamline administrative tasks and create a more engaging, personalized experience for new employees. For example, it can improve and speed up processes such as scheduling meetings and sending invitations. AI can significantly reduce the time and resources spent on traditional onboarding, allowing HR teams to focus on higher-value tasks, such as cultural integration and team-building.
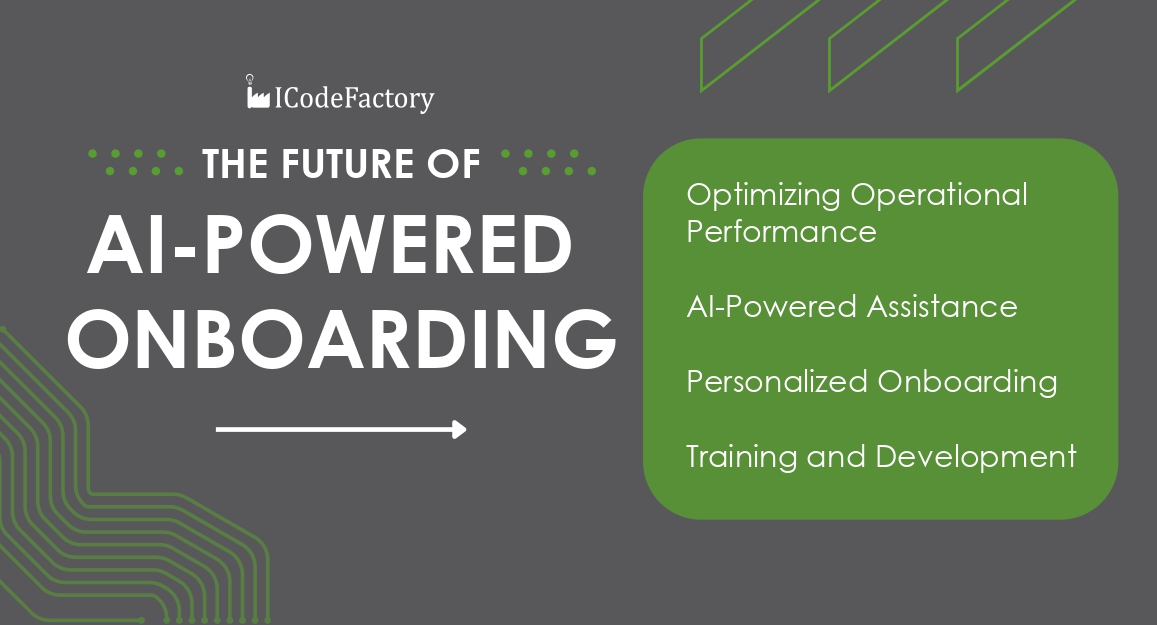
Key AI Solutions for Effective Onboarding:
Optimizing Operational Performance: The first area of improvement involves enhancing operational performance by providing new hires with a link to the new employee portal. Through this portal, they can access essential company information, such as the code of conduct and ethical guidelines. It also provides details on orientation programs, employee benefits packages, and the necessary forms for submission. With the help of automated tools, new employees are guided to key resources and milestones in the hiring process. This system aids their integration in the early days, allowing them to focus more on connecting with their team and adapting to the company culture.
AI-Powered Assistance: By implementing AI-powered chatbots, organizations can provide new hires with immediate answers to frequently asked questions, reducing the need for constant HR intervention. This automation not only speeds up the onboarding process but also enhances employee satisfaction by offering real-time support.
Personalized Onboarding: Experts agree that onboarding should be tailored to each new employee's skills, personality, and preferences. AI can handle large amounts of data, making it easier to customize the onboarding experience. For example, intelligent systems can suggest appropriate training programs or resources tailored to the employee's skills, helping to address any skill gaps.
Training and Development: Machine learning models can predict the skills new hires will need to develop, offering targeted training programs that align with their individual growth potential. This results in better-prepared employees who are more likely to succeed and stay within the organization.
Challenges
While AI offers substantial benefits in onboarding, it also presents several challenges. One key issue is the potential lack of human touch and empathy in the process, which can make new employees feel disconnected. Additionally, AI-driven solutions rely heavily on data accuracy; poor data quality can lead to ineffective or misleading recommendations. There is also the risk of resistance from employees and HR teams who may be unfamiliar or uncomfortable with AI-based systems. Privacy concerns surrounding employee data must also be carefully managed to maintain trust and compliance with regulations. Finally, implementing AI onboarding solutions requires significant investment in both technology and training, which can be a barrier for some organizations.
Conclusion
AI-powered onboarding comes with its challenges. However, the key is finding the optimal balance with AI onboarding while keeping the human touch at the core. When done right, with the AI-driven strategies, challenges can be effectively addressed.
The real question is, are you ready for changes in HR operations and team dynamics?
Ready to take the next step?
Let's explore how our expertise can help you innovate and implement your vision in a digital world.
Reach out to us:ICodeFactory | Contact
22/04/2025
The pressure to rapidly acquire new skills and adapt to technological advances has never been greater. Traditional training methods—often characterized by lengthy, one-size-fits-all programs—are increasingly seen as inefficient, overwhelming, and disconnected from the realities of modern work. When change is constant, learning must be smarter. As attention spans shrink and the pace of change accelerates, organizations must seek innovative solutions that not only deliver critical knowledge quickly but also foster a culture of continuous learning. This is where microlearning comes into play—a transformative, bite-sized approach to education that fits seamlessly into the busy schedules of today’s workforce.
Recent studies further emphasize the transformative impact of microlearning. Research conducted by the Society for Human Resource Management found that companies implementing microlearning have experienced an impressive 130% boost in employee engagement and productivity compared to those relying solely on traditional training methods.
What Is Microlearning and Why Does It Work?
According to Harvard Business Review, microlearning is a training method that delivers content in short, focused bursts, making it ideally suited for the fast-paced demands of the modern workplace. Instead of dedicating hours to traditional classroom-style sessions, employees can now access focused modules—whether it’s a five-minute tutorial, an interactive quiz, or a concise video lesson—tailored to specific learning objectives. This method not only addresses the inefficiencies of conventional training, but also aligns with the way our brains are wired to process and retain information. By breaking down complex subjects into manageable segments, microlearning makes the acquisition of new skills both approachable and engaging.
Science provides a solid foundation for this approach. Hermann Ebbinghaus’s Forgetting Curve illustrates that without reinforcement, nearly 50% of new information is forgotten within the first hour, and up to 80% can vanish within days. Microlearning leverages principles such as spaced repetition and just-in-time learning to counteract this rapid decline in memory retention. By delivering information in short, repetitive intervals, employees are more likely to internalize and apply what they learn, ultimately resulting in a more competent and confident workforce. This scientific backing not only underscores the effectiveness of microlearning but also provides decision-makers with a clear rationale for embracing this method.
Beyond science, the practical benefits of microlearning are compelling. For instance, employees can engage in quick learning sessions that seamlessly integrate with their daily work routines, reducing the disruption often caused by prolonged training programs. This on-the-go accessibility means that learning is no longer confined to scheduled training sessions; it becomes an integral part of the workday, empowering staff to develop skills as and when needed. Moreover, microlearning serves as both a standalone solution and a valuable supplement to traditional training, making it versatile enough to address a wide range of learning needs across industries such as healthcare, technology, finance, and more.
Scalability as an Imperative for the Modern Enterprise
A key advantage of microlearning is its scalability. Scalable training solutions can be easily implemented across diverse departments and geographical locations, making them ideal for global enterprises. Whether it’s technical training for IT teams, leadership development for managers, or compliance education for employees navigating different regulatory environments, microlearning ensures that training remains consistent, accessible, and adaptable across the entire organization. This capability for standardized yet customizable delivery of knowledge not only streamlines the training process but also ensures that every employee, regardless of location or role, receives high-quality, relevant content.

A Smart Investment in Workforce Agility
Investing in microlearning isn’t merely about keeping pace with current trends—it’s a strategic imperative for future-proofing your workforce. By embracing microlearning, companies can cultivate an agile, continuously learning environment that is ready to tackle the challenges of tomorrow. The return on investment (ROI) for microlearning is evident in both its cost-effectiveness and its positive impact on workforce agility. By reducing the need for lengthy, resource-intensive training sessions, companies can minimize downtime and lower training costs while still delivering high-quality, effective learning experiences. In an environment where rapid adaptation is key, the ability to learn and apply new skills quickly is a decisive competitive advantage. Moreover, microlearning supports personalized learning paths, enabling employees to focus on the skills most relevant to their roles and career growth—further enhancing overall productivity and job satisfaction.
Now is the time to rethink your training strategy, invest in microlearning, and enable your workforce to thrive in tomorrow’s (or even today's?) marketplace.
Ready to take the next step?
Let's explore how our expertise can help you innovate and implement your vision in a digital world.
Reach out to us:ICodeFactory | Contact
18/03/2025
Excess inventory and waste – How much is it costing you? Businesses worldwide lose trillions of dollars each year due to inefficient inventory management according to a report from IHL Group. In industries such as retail and manufacturing excess stock and unnecessary waste are not only a financial issue but also an environmental challenge.
To address these issues, predictive analytics emerges as a key tool for resource optimization. By leveraging advanced algorithms and data, predictive analytics enables businesses to more accurately forecast demand, reduce excess stock, lower costs, and minimize their environmental footprint. Implementing this technology allows companies to achieve more efficient operations and build a more sustainable business model, which is important for future success in an increasingly competitive market.
-(1).jpg)
Key Strategies for Reducing Waste and Costs with Predictive Analytics
1. Predict Demand Precisely
Accurate demand forecasting can be achieved by identifying demand patterns and incorporating external factors like market trends and economic conditions. Predictive models, such as time series and regression analysis, improve prediction accuracy.
2. Optimize Inventory Efficiency
Predictive analytics can help calculate optimal inventory levels by factoring in forecasted demand and lead times. Implementing safety stock ensures preparedness for demand fluctuations or supply disruptions. Regularly reviewing inventory turnover rates helps adjust stock levels to avoid overstocking and minimize storage costs.
3. Reduce Obsolete Inventory
To reduce obsolete inventory, predictive analytics can be used to identify slow-moving products, enabling actions like discounts or redistribution to prevent excess stock. Implementing Just-in-Time (JIT) inventory practices minimizes holding costs and the risk of obsolescence by relying on accurate demand forecasts and timely replenishment.
Predictive Analytics in Various Industries
For example, in the retail industry, predictive analytics allows companies to forecast consumer behaviour with greater accuracy. By analyzing historical sales data, market trends, that products are available when needed, without risking excess stock that could end up as waste. Manufacturers are also making the most of predictive tools to optimize production processes. By forecasting demand for raw materials and finished products, they can avoid overproduction and minimize the risk of holding surplus inventory. This not only reduces waste but also enhances production efficiency. Logistics companies are benefiting from predictive analytics by optimizing inventory management across locations. By forecasting demand and optimizing supply chain routes, they avoid overstocking and inefficiencies, leading to fewer delays, reduced waste, and cost savings.
Example: Predictive Analytics in Manufacturing
A global industrial manufacturer, faced challenges with tool management, leading to increased costs and production downtime. Tools were difficult to track, often resulting in wasted time searching for them, and worn-out tools were sometimes used beyond their lifespan, causing unexpected breakdowns and delays.
With the implementation of tool data management software with predictive analytics, the company was able to analyze tool usage data, predict when a tool would reach the end of its useful life, and reduce unscheduled downtimes. Predictive models analyzed historical data on tool usage and machine load, enabling timely replacement of tools before they became unusable, thus minimizing production interruptions.
Within the first six months of using tool data management solution and predictive analytics, the company reduced downtime by 15% and lowered tool-related costs by 20%. By optimizing production schedules and monitoring tool conditions, the company reduced excess inventory, minimized waste, and improved overall resource efficiency.
Is excess inventory and waste quietly draining your profits? If you want to reduce costs and eliminate waste, now is the right time to explore predictive analytics.
Ready to take the next step?
Let's explore how our expertise can help you innovate and implement your vision in a digital world.
Reach out to us:ICodeFactory | Contact
27/02/2025
Having spent years in banking, I’ve experienced the constant challenges of managing complex data effectively in a highly regulated environment.
How to handle sensitive client data? How to ensure compliance with regulations? How to make complex real-time data available quickly and easily? How to empower non-technical teams to perform advanced analytics without engagement of IT team resources?
Transitioning into IT industry, I found Microsoft Fabric to be the answer. It is a perfect digital solution that addresses all these challenges, while simplifying access to data for employees across various banking functions.
How can Fabric do that?
Because Microsoft Fabric is an end-to-end analytics and data platform designed for enterprises that require a unified solution. It encompasses data movement, processing, ingestion, transformation, real-time event routing, and report building
Let’s analyze some examples together:
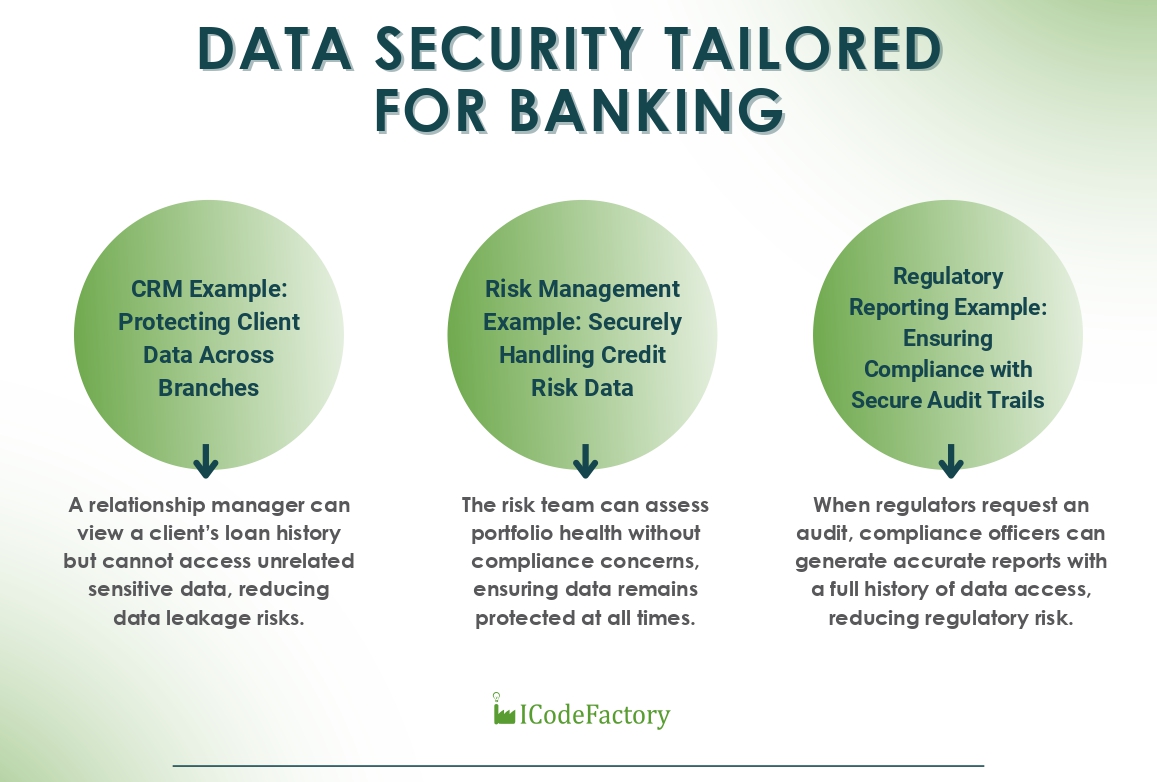
1. DATA SECURITY TAILORED FOR BANKING
Data security is at the core of any banking operation, and Microsoft Fabric provides the highest level of robust data protection. With end-to-end encryption, role-based access control, and compliance with standards like GDPR, it ensures that data is always secure.
CRM Example: Protecting Client Data Across Branches
Banks operate across multiple branches, often sharing client data between relationship managers and central teams. With Fabric’s granular access controls, only authorized employees can access specific client records, ensuring privacy and preventing unauthorized data exposure.
- Outcome: A relationship manager can view a client’s loan history but cannot access unrelated sensitive data, reducing data leakage risks.
Risk Management Example: Securely Handling Credit Risk Data
A risk management team analyzing loan default trends can access sensitive credit data while ensuring that client details remain protected, anonymized, and accessible only to authorized employees. This helps maintain compliance and trust while enabling deeper insights.
- Outcome: The risk team can assess portfolio health without compliance concerns, ensuring data remains protected at all times.
Regulatory Reporting Example: Ensuring Compliance with Secure Audit Trails
Regulatory bodies require banks to maintain detailed records of financial transactions and risk assessments. Fabric automatically logs all data interactions, creating a secure audit trail for compliance reviews.
- Outcome: When regulators request an audit, compliance officers can generate accurate reports with a full history of data access, reducing regulatory risk.
2. REAL-TIME DATA INSIGHTS FOR SMARTER LOAN PORTFOLIO MANAGEMENT
Fabric seamlessly integrates data from multiple sources—loan origination models, portfolio management systems, CRM platforms, and external credit reports, providing a unified view for advanced analytics and real-time reporting.
CRM Example: Identifying High-Value Clients
Imagine your CRM and Risk teams want to identify low-risk clients with the potential for cross-selling or top-up their loan products. Using Fabric, they can combine portfolio data, transactional history, repayment behavior, and demographic information to create advanced dashboards that highlight potential cross-selling opportunities. This data can be integrated as sales support tools in a bank’s branch network or be a valuable input for sales campaigns through digital (Mobile or Internet) banking channels.
- Outcome: Relationship managers can provide the best customer experience to high-value clients, improving loan origination efficiency and increasing growth. Digital channel campaigns can be easily targeted at the best client segments to minimize risk and maximize profit.
Risk Management Example: Modeling Probability of Default
Risk teams need to assess loan portfolio quality and predict potentially high-risk segments with increased Probability of Default. With Fabric, they can seamlessly integrate historical repayment data, DPD delinquency vintage data, behavior information, transactional data, and macroeconomic indicators to build robust statistical PD models.
- Outcome: The system highlights loans with a high risk of default, enabling proactive measures both ex-post <such as restructuring offers or early collection on existing portfolios> and ex-ante <such as restrictions on future loan activities within identified problematic client segments>.
Regulatory Reporting Example: Ensuring reporting compliance with standard’s requirements (red: standard requirements)
Fabric simplifies the preparation of regulatory reports, such as those required for Basel III compliance. It can aggregate data on capital adequacy, liquidity coverage, and credit exposure from multiple systems into pre-configured templates.
- Outcome: Regulatory and statutory reporting teams can generate and submit accurate, audit-proof reports in hours instead of days, reducing operational risk and increasing efficiency.
3. MAKING ADVANCED ANALYTICS ACCESSIBLE TO ALL TEAMS
One of Fabric’s standout features is its user-friendly interface, enabling even non-technical staff to work with complex data.
CRM Use Case: Self-Service Reporting for Managers
A regional branch manager wants to analyze loan disbursement trends. Using Power BI within Fabric, they can drag and drop metrics like loan types, approval rates, sales rates, CRM lead conversions, and demographics data to create a detailed breakdown and analysis of sales results.
- Outcome: Managers quickly and easily gain actionable insights without relying on or waiting for IT, enabling fast and high quality decision-making.
Risk Management Use Case: Scenario Analysis and Stress-Testing
Risk analysts can use Fabric to simulate "what-if" scenarios, such as the impact of an economic downturn on a loan portfolio IT independently, quick and easy.
- Outcome: These simulations are easy to create in Fabric without IT assistance, providing a data-driven foundation for adjusting credit policies, planning provisions, and mitigating potential losses or budget breaches related to risk costs.
Regulatory Reporting Use Case: Automating Data Pipelines
Fabric automates the data aggregation process for regulatory filings, such as those for anti-money laundering (AML).
- Outcome: AML compliance officers can focus on analysis and oversight instead of manual data gathering, ensuring deadlines are met efficiently.
4. SEAMLESS COLLABORATION ACROSS TEAMS
Fabric’s cloud-native environment ensures that all teams in the Bank—like Sales, CRM, Risk Management, Portfolio Monitoring, Compliance, Finance, etc.—work from a single source of truth, eliminating data silos.
Example:
A Portfolio Monitoring officer reviewing reports notices unusual credit portfolio trends with Fabric. They can instantly share insights with the Risk Management team, who can drill down into the same data set, to identify underlying causes and adjust credit policies.

5. CONCLUSION
Microsoft Fabric is a transformative platform for banking, offering tailored solutions.
It combines security, advanced analytics, and a user-friendly approach for non-IT users.
From identifying cross-selling opportunities, predicting loan defaults, and ensuring compliance with regulatory standards, Fabric provides digital tool banks need to operate smarter and more effectively in an increasingly complex and competitive landscape.
If you are facing these challenges and want to address them with state-of-the-art data management tool which contains comprehensive suite of services including Data Engineering, Data Factory, Data Science, Real-Time Analytics, Data Warehouse, and Databases, contact us!
As Microsoft Partner we can support you both in implementation and trainings for MS Fabric.
Cetko Okiljevic
Head of Digital Financial Solutions @ ICodeFactory
Looking for more information? Reach out to us:ICodeFactory | Contact










-(1).jpg)

